Congratulations! You’ve reached a significant milestone in your career – retirement. As you begin this exciting new chapter, it’s essential to make wise decisions about your financial future. In this article, we’ll explore the world of retirement investments for employees, where you can discover the various options available to help secure a comfortable and rewarding retirement. From 401(k) plans to IRAs and employer-sponsored programs, we’ll provide valuable insights to empower you as you embark on this journey towards financial independence. So, let’s dive in and uncover the possibilities that await you in the realm of retirement investments for employees.
Retirement Investments For Employees
If you’re an employee, planning for retirement is crucial in order to ensure financial security in your golden years. One of the key steps in this process is selecting the right retirement investments that align with your goals and risk tolerance. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various options for retirement investments, types of retirement accounts, investment strategies, risks and considerations, and the significance of employer-sponsored retirement plans. Additionally, we will discuss supplementary sources of income such as Social Security benefits, rental income, and real estate investments. So let’s dive in and start planning for a comfortable retirement!
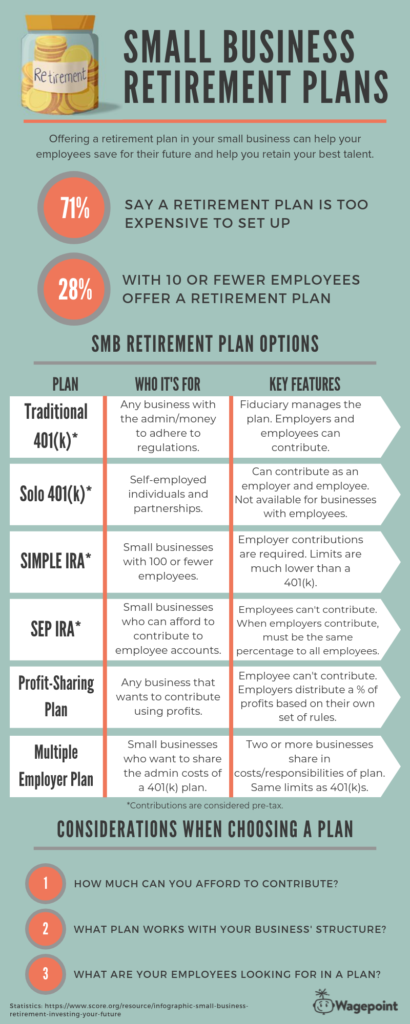
This image is property of smallbizclub.com.
Options for Retirement Investments
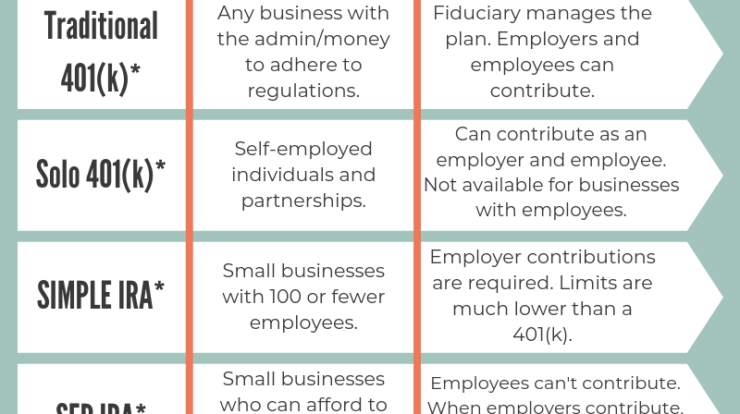
When it comes to retirement investments, employees have a wide array of options to choose from. These options include retirement accounts such as 401(k) accounts, Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), Roth IRAs, Simplified Employee Pension Plans (SEP IRAs), 403(b) accounts, Thrift Savings Plans (TSP), and pension plans. Each of these options comes with its own set of features and benefits, so it’s important to understand them in order to make an informed decision.
Types of Retirement Accounts
1. 401(k) Accounts
401(k) accounts are one of the most common retirement accounts offered by employers. They allow you to contribute a percentage of your salary on a pre-tax basis, which means you don’t have to pay taxes on the contributed amount until you withdraw the funds in retirement. Some employers also offer matching contributions, which is essentially free money towards your retirement savings.
2. Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
IRAs are retirement accounts that individuals can set up on their own. They offer a range of investment options such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Contributions to traditional IRAs may be tax deductible depending on your income level, while contributions to Roth IRAs are made with after-tax dollars. Withdrawals from traditional IRAs are taxed in retirement, whereas qualified withdrawals from Roth IRAs are tax-free.
3. Roth IRA
Similar to a traditional IRA, a Roth IRA is an individual retirement account. However, contributions to Roth IRAs are made with after-tax dollars, meaning that withdrawals in retirement are generally tax-free. Roth IRAs are a great option for those who anticipate being in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
4. Simplified Employee Pension Plan (SEP IRA)
A SEP IRA is specifically designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners. It allows you to make tax-deductible contributions to a retirement account on behalf of yourself and your employees, if applicable. SEP IRAs offer flexibility and can be a great choice for those who are self-employed or own a small business.
5. 403(b) Accounts
403(b) accounts are retirement accounts typically offered to employees of educational institutions, non-profit organizations, and certain healthcare providers. Contributions to 403(b) accounts are made with pre-tax dollars, similar to 401(k) accounts. These accounts provide a great way for employees in these sectors to save for retirement.
6. Thrift Savings Plan (TSP)
The Thrift Savings Plan, commonly known as TSP, is a retirement savings plan available to Federal employees and members of the uniformed services. It offers a variety of investment options and contributions can be made on a pre-tax or after-tax basis. TSP is known for its low fees and flexibility, making it an attractive choice for those who work in the public sector.
7. Pension Plans
Pension plans are a traditional form of retirement benefit provided by some employers. With a pension plan, employees receive a fixed sum of money each month in retirement based on factors such as years of service and salary history. While pension plans are less common nowadays, they can provide a reliable source of retirement income for employees fortunate enough to have them.

This image is property of www.investopedia.com.
Investment Strategies for Retirement
Now that we have covered the different types of retirement accounts, let’s explore some essential investment strategies that can help you maximize your retirement savings and achieve your financial goals. These strategies include diversification, asset allocation, regular contributions, rebalancing, and seeking professional financial advice.
1. Diversification
Diversification is a fundamental strategy in retirement investing. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, you can reduce the impact of market volatility on your portfolio. This strategy helps to balance the potential risks and returns in your retirement investments.
2. Asset Allocation
Asset allocation refers to the distribution of your investments among different asset classes. It involves determining the appropriate mix of stocks, bonds, and other investment vehicles based on your risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. Asset allocation allows you to achieve a balance between growth and stability in your retirement portfolio.
3. Regular Contributions
Making regular contributions to your retirement accounts is crucial for long-term wealth accumulation. By contributing a fixed amount from each paycheck, you are consistently building your retirement savings over time. This strategy takes advantage of compounding interest, which can significantly boost the growth of your investments over the years.
4. Rebalancing
As the market fluctuates, the proportions of your investments within different asset classes may shift. Rebalancing involves periodically reviewing your portfolio and adjusting the allocation of your investments to maintain your desired asset mix. This ensures that your investments remain aligned with your long-term goals and risk tolerance.
5. Professional Financial Advice
Navigating the world of retirement investments can be complex, and seeking professional financial advice can provide valuable guidance. A financial advisor can help you assess your goals, develop a customized retirement investment plan, and provide ongoing support and monitoring of your portfolio. Professional advice can help you make informed decisions and optimize your retirement investments.
Retirement Investment Risks and Considerations
While retirement investments offer the potential for growth and financial security, they also come with risks and considerations that need to be carefully evaluated. Let’s explore some of the key factors to consider when planning for retirement.
1. Market Volatility
Market volatility refers to the fluctuations in the value of investment assets due to changes in market conditions. Investing in the stock market can be rewarding, but it also involves exposure to market volatility. It’s important to understand that the value of your investments may fluctuate over time and to have a long-term perspective when dealing with market volatility.
2. Inflation
Inflation is the increase in the prices of goods and services over time, eroding the purchasing power of your money. When planning for retirement, it’s essential to consider the impact of inflation on your retirement investments. Investing in assets that provide a hedge against inflation, such as stocks and real estate, can help safeguard your retirement savings against the effects of rising prices.
3. Taxes
Taxes can have a significant impact on your retirement investments. It’s important to understand the tax implications of different retirement accounts and investment vehicles. For example, withdrawals from traditional IRAs and 401(k) accounts are typically subject to income taxes, whereas qualified withdrawals from Roth IRAs are generally tax-free. Working with a tax advisor can help you minimize your tax liability and optimize your retirement savings.
4. Longevity Risk
Longevity risk refers to the possibility of outliving your retirement savings. With advancements in healthcare and lifestyles, people are living longer than ever before. It’s crucial to carefully plan and ensure that your retirement investments can sustain you throughout your retirement years. This may involve conservative withdrawal strategies and accounting for rising healthcare costs.
5. Withdrawal Strategies
Determining the best withdrawal strategy for your retirement investments is an important consideration. Some retirees choose to withdraw a fixed percentage each year, while others opt for more flexible approaches, such as the 4% rule. It’s important to align your withdrawal strategy with your financial goals, risk tolerance, and other sources of income to ensure a sustainable and comfortable retirement.

This image is property of m.foolcdn.com.
Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans
Many employers offer retirement plans to their employees as part of their benefits package. These employer-sponsored retirement plans can play a significant role in helping employees save for retirement. Let’s explore some key features and considerations of these plans.
1. Matching Contributions
One of the most attractive features of employer-sponsored retirement plans is the opportunity for matching contributions. This means that your employer will contribute a certain percentage of your salary to your retirement account, often matching a portion of your own contributions. Matching contributions essentially provide free money towards your retirement savings, making employer-sponsored plans highly advantageous.
2. Vesting Schedules
Vesting schedules determine when you have full ownership of the employer’s contributions to your retirement account. Some employers have immediate vesting, meaning you gain full ownership of their contributions right away. Others may have a graded or cliff vesting schedule, where ownership increases gradually over time or after a certain number of years of service. It’s important to understand the vesting schedule of your employer’s retirement plan to maximize the benefits.
3. Employer Stock
Some retirement plans allow employees to invest in the company’s stock. While this can be an appealing option, it’s important to carefully evaluate the risks associated with having too much exposure to a single company. Diversification is crucial to mitigate the risk of company-specific events impacting the value of your retirement investments.
Supplementing Retirement Investments
While your primary focus may be on retirement investments, it’s important to consider supplementary sources of income that can enhance your financial security during retirement. Let’s explore a few options for supplementing your retirement investments.
1. Social Security Benefits
Social Security benefits play a significant role in the retirement income of many individuals. These benefits are based on your earnings history and the age at which you claim them. Understanding how Social Security works and optimizing your claim strategy can help maximize the benefits you receive during retirement.
2. Rental Income
Investing in rental properties can provide a steady stream of income in retirement. This can be a particularly attractive option for those who have a knack for real estate and are willing to take on the responsibilities of being a landlord. Rental income can supplement your retirement investments and provide a reliable source of income.
3. Real Estate Investments
Apart from rental properties, other forms of real estate investments, such as real estate investment trusts (REITs) or real estate crowdfunding platforms, can offer attractive long-term returns. Real estate investments can provide both income and appreciation potential, diversifying your retirement portfolio and enhancing your overall financial position.
4. Annuities
Annuities are financial products that provide a steady stream of income over a specified period of time, typically for the rest of your life. They can be purchased from insurance companies and offer a way to ensure a guaranteed income stream during retirement. Annuities can be a suitable option for those seeking to supplement their retirement investments with a reliable income source.
In conclusion, retirement investments for employees are a critical element of financial planning. By exploring the options available for retirement accounts, understanding investment strategies, evaluating risks and considerations, and considering supplementary sources of income, you can lay a solid foundation for a comfortable and financially secure retirement. Remember, it’s never too early or too late to start planning for your future, so take the first step today and set yourself up for a fulfilling retirement journey.









